In this article, we will discuss EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol), which is a hybrid routing protocol. It was originally defined by Cisco and available on only Cisco devices. Since 2013, it’s now an Open Standard and defined in RFC 7868. EIGRP works on the Network Layer of the OSI Model and the protocol number is 88.

Quick Overview of EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
EIGRP stands for Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol. In 1993, IGRP (Interior Gateway Routing Protocol), is replaced by EIGRP, because IGRP doesn’t support IPv4 classless routing. EIGRP is the combination of Distance Vector (RIP) and Link State (OSPF) routing protocols. Thus, the EIGRP protocol is known as Advance Distance Vector or Hybrid routing protocol.
EIGRP is a dynamic routing protocol, which is used to share routes/ prefix information to neighboring routers. Unlike RIP, EIGRP only sends triggered updates to neighbor routers.
Different types of Tables used in EIGRP
Unlike RIP, EIGRP has Neighbor Table and Topology Table in addition to the Routing Table. We will discuss all these tables one by one.
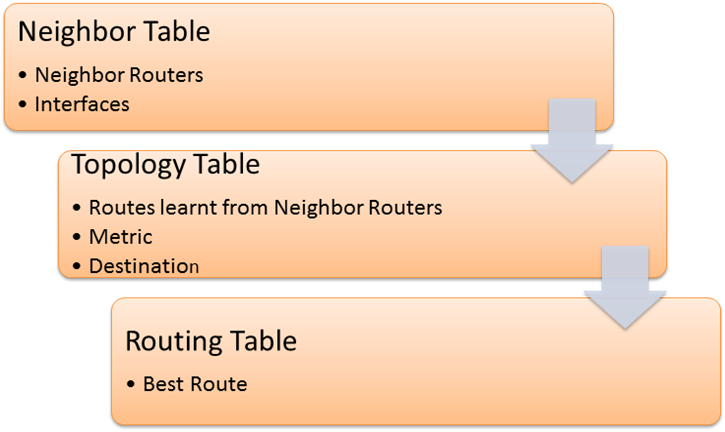
Routing Table
The purpose of the EIGRP Routing Table is the same as other routing protocols. A router makes a forwarding decision based on the Routing Table. The best route from the topology table is transferred in the Routing Table.
Topology Table
The topology table has various routes which are learned from different neighbor routers. This contains detailed information about the routes like Metric, Destination. Unlike the routing table, the route of the topology table never participated in routing. However, the Topology Table has backup routes. If the router lost their best route from their routing table, then the topology table provides the backup path as the best path to the routing table.
The best path of Topology Table is used in the Routing Table.
Neighbor Table
Neighbor Table, as the name suggests, has detailed information about neighbor routers that are directly connected. However, it does not contain any information about indirectly connected routers.
EIGRP Metric Calculation
Unlike RIP, the metric of any route in EIGRP depends upon any parameters. In fact, EIGRP uses 6 different parameters to calculate the matrix. These parameters are Bandwidth, Load, Total Delay, Reliability, MTU, and Hop Count. By default, minimum Bandwidth and Total Delay are used for Metric calculation. But, an administrator can use all these parameters to calculate the route’s metric. These parameters are known as K-Values.
Features of EIGRP Protocol
EIGRP uses the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL), which helps to calculate the best feasible successor and also prevents routing loops. It supports both Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM). It can support Unequal Cost Load Balancing with the help of variance command. We can also apply authentication for security reasons. Unlike RIP, sends only triggered update, not full update.
Related Articles
- EIGRP Packet Types and Neighborship Parameters
- OSPF Neighborship States
- OSPF Packets Types and Neighborship Parameters
Summary
In this article, we discussed the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). There are three different tables used in EIGRP. All routes are present in the Topology Table. However, the best routes of the Topology Table are copied into the Routing Table. For reliability purposes, it uses RTP (Real-Time Trunking Protocol).
Did you find this article helpful? Please leave a comment in the comment box!