Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is one of the famous routing protocols. It is widely used in networking. In this article, we will discuss types of messages/ packets which is used in the EIGRP Protocol. We will also discuss the EIGRP parameter which is required to become an EIGRP neighbor.

Quick Overview of EIGRP Messages
Before moving to the detailed discussion of EIGRP Messages/Packets, let’s take a quick look on EIGRP Messages:
- Hello
- Update
- Query
- Reply
- Acknowledgment
Hello
Hello, the message is the first message which is sent to a neighbor router in order to become an EIGRP neighbor. In EIGRP, Hello message is responsible for:
- Hello, the message is used for neighbor discovery.
- It is used for Keep alive purpose.
- It is always multicast on every type of link.
- Hello, the timer is 5 seconds and it is periodically sent.
- Hold down timer is 15 seconds.
However, several different contents also send in an EIGRP Hello message. Let’s take a look at EIGRP Hello Message which is captured by Wireshark.
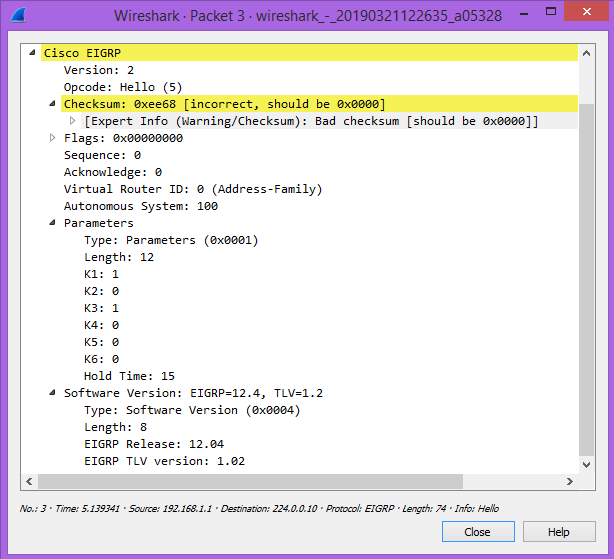
According to the captured packet, the contents of EIGRP Hello Message:
- Version (v2 by default)
- Opcode 5
- Checksum
- Sequence Number and Acknowledgement number
- Autonomous Number (depends upon the EIGRP process)
- K-Values (by default K1, K3)
- Hold Down Timer
- IOS Version
- Authentication
You can also read: OSPF Packets Types
Update Message
The update message is sent between neighbors to build the topology table and routing table. Basically, the OSPF neighbor router shares their prefix to their neighbor with the help of Update Message. Update messages can be Multicast and Unicast. On the serial link, the update message is Unicast. However, in the Ethernet link, it can be Multicast and Unicast. The opcode of Update Message is 1. It also contains an Autonomous Number. Update messages used RTP (Reliable Transport Protocol) to make packets reliable. Sequence and Acknowledgement number are used in Update Message.
So, Update Message has the following property:
- Can be Unicast/Multicast
- Opcode 1
- Sequence Number and Acknowledgement Number
- Autonomous Number
- Metric (K1, K2, K3, K4, K5)
- Subnet Information
Query Message
As the name suggests, Query Packets are sent when a successor route fails and there is no feasible successor in the EIGRP topology table. The Router who lost the route sends a query message for asking their neighbor that the same route is present or not on their topology table. The maximum delay time is also set in Query Message. It is always Unicast at serial link and Multicast on Ethernet link. Properties of Query Message:
- Opcode 3
- Can be Unicast or Multicast
- Use RTP (Reliable Trunking Protocol)
- Have Sequence and Acknowledge numbers
Reply Message
Reply Message is sent in the response of Query Message. The responding router has an alternate route in their topology table and that router reply the query of the neighbor router. Like Update and Query message, the Reply message is also used RTP. They also use sequence and acknowledgment numbers. Properties of Reply Message:
- Opcode 4.
- Use RTP.
- It is always a Unicast Message.
Acknowledgment Message
As the name suggests, this message is an acknowledgment for Update, Query and Reply messages. It is not used in the EIGRP Hello message. The opcode of the EIGRP Acknowledgement Message is 5.
Neighborship Parameters
To become an EIGRP neighbor, there are several conditions that must be common. They are:
- Autonomous Number must match
- K-Values must match
- Authentication must match (optional)
- Network-ID must match
Summary
In this article, we discussed various EIGRP messages. However, a Hello message is used for neighbor discovery and neighbor formation process. Update, Query and Reply messages are used RTP and thus they are reliable messages. We also discussed some parameters which must be common in order to become an EIGRP Neighbor.
Did you find this article helpful? Please leave a comment in the comment box.